A data center is a building or group of buildings dedicated to hosting computer systems and their associated components. These components include storage systems and telecommunications.
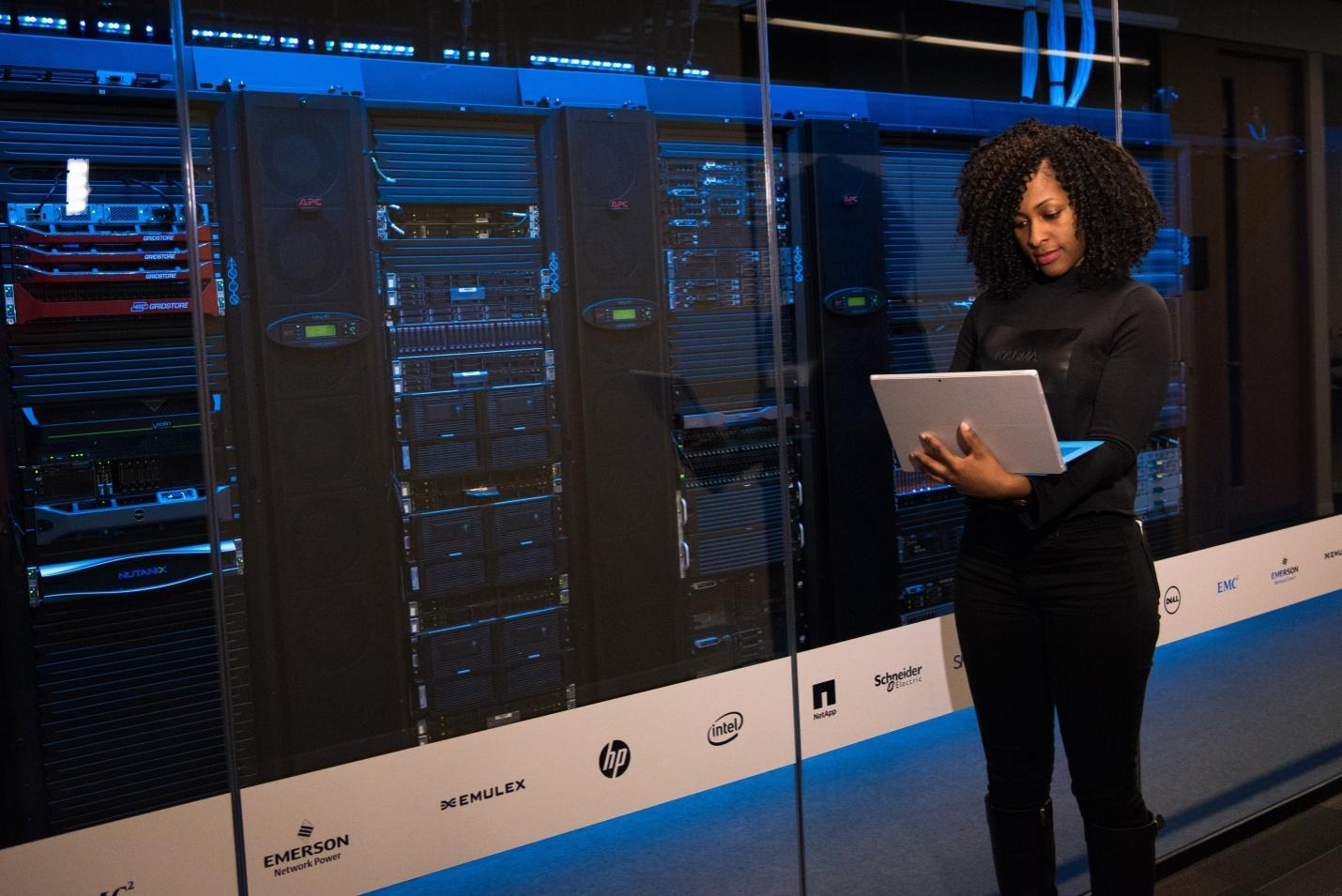

Data centers are often located in a secure area, and they provide a variety of benefits to their tenants. In addition to allowing for a more efficient use of space, a data center can be highly secure and offers high levels of data protection.
Keeping servers cool
Data centers have multiple cooling options, including air-source heat pumps (ASHPs), air-conditioning, or a combination of both. Click here for more information about ASHPs.
To keep server temperatures manageable, engineers design computer rooms with cold and hot aisles. The cold aisle is designed to provide cool air to the front of the racks, while the hot aisle is intended for warm air. The cooling system also includes a dedicated cooling unit, which is monitored and serviced 24 hours a day.
Keeping data center servers cool is essential for the health and performance of IT equipment. Without effective cooling, temperatures can increase, causing equipment failure.
Additionally, servers can slow down processing speed if they overheat. Proper airflow management will reduce the burden on air conditioning systems in the building.
Data centers can use outside air to keep server temperatures down, and some even use ocean water for cooling. However, many are not running at peak efficiency.
The power consumption effectiveness (PUE) of a data center reflects power coming into the data center and how evenly it is distributed throughout the workload.
The biggest opportunity for IT managers is to monitor hardware components. By monitoring and regulating the temperature of server racks, IT managers can improve the efficiency of their data centers.
Keeping data center servers cool is important to the health of IT equipment, but it can be expensive to manage. IT managers must also keep energy costs under control.
Also Read: Why Are HPC Containers Better Than VMs?
Providing fault tolerance and redundancy

Providing fault tolerance and redundancy on your data center server is critical if you are going to ensure uninterrupted operations.
This is possible with many different methods. For example, you can implement a Distributed Replicated Block Device, or DRBD, which mirrors information between two servers to maintain synchronicity.
You can also implement a Heartbeat infrastructure, which monitors and sends messages in case of server failure. This ensures minimal interruptions to your users’ workflows.
Providing fault tolerance and redundancy on your information-localized server requires extra equipment, specialized monitoring, and information-localized space.
The additional hardware and maintenance can increase your costs. It’s important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks before deciding on a system.
Redundancy can also be implemented as a system design principle, with components duplicated to minimize the risk of a failure and restore service to a stable state.
It also provides protection against abnormal behavior. There are different types of redundancy, each suited to a specific business model.
Providing fault tolerance and redundancy is important for business continuity. Downtime can impact a company’s operations, brand image, and customer experience, and can cost hundreds of dollars a minute.
Providing fault tolerance and redundancy in your information localized computer is an effective way to minimize this risk. Redundant configurations minimize the risk of unscheduled downtime, and the resiliency of redundant components ensures the safety and integrity of information.
Providing fault tolerance and redundancy on your information localized computer will ensure minimal disruption of business operations.
High availability is a necessary part of information localized machine design, and it provides an automatic failover in the event of a failure. By providing multiple systems with identical information, you can reduce the risk of downtime and keep your business running smoothly.
Also Read: What is a VPS Server and where they are used?
Protecting network security and application delivery assurance
Data localized computers offer a number of benefits, including application resilience and performance, and increased security.
The best servers, like the ones found here: https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/servers-storage/, are equipped with firewalls and other tools that prevent hacker attacks and protect data.
They also help maintain application resilience and availability through automatic failover protocols and load balancing.
Data localizations have multiple levels of protection, including physical security, surveillance, and multifactor authentication.
For instance, information localizations must have strict controls on the use of electronic devices. In addition, physical access to the information localization should be controlled.
Server racks should be locked to prevent unauthorized access. This prevents the risk of information leakage and physical disruptions.
The infrastructure of information localization includes servers, switches, and routers that are used to store and process large amounts of information. They also support network applications and improve network performance.
Because information localizations are the nerve localization of an organization, they must be protected. A number of factors must be taken into account, including the number of people working in them, the type of information localization, and the location.









+ There are no comments
Add yours